Potential pathways for utilisation of spent FCC catalyst from Dung Quat refinery
Abstract
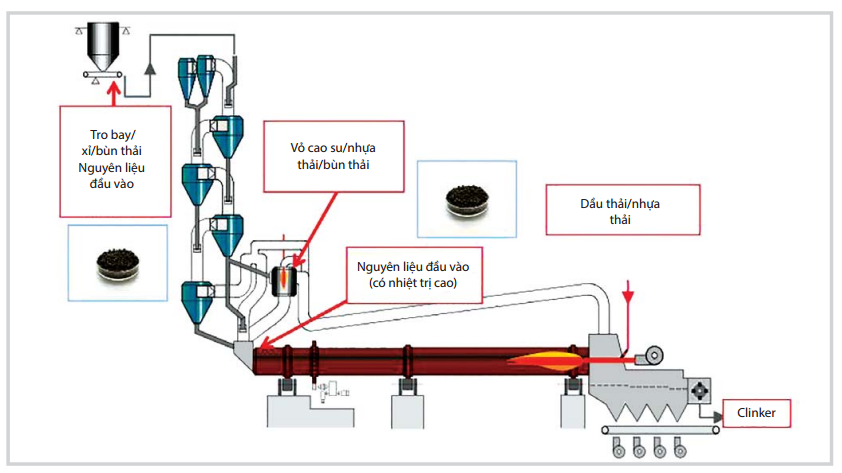
The paper evaluates some pathways to recycle spent FCC catalyst at Dung Quat Refinery, with focus on some options to thoroughly utilise the spent FCC catalyst in a sustainable way, especially as building material. The results of testing in the laboratory and field survey show that the feasible pathways are ranked by spent catalyst recycling capacity as follows: raw material for cement production (20 - 200tons/day), pozzolanic material for cement additive production (> 15 tons/day), clay for red brick production (15 tons/day), and cement for concrete block production (11 - 17 tons/day).
References
2. Hoàng Văn Phong. 20 chủng loại xi măng và công nghệ sản xuất. Nhà xuất bản Khoa học Kỹ thuật. 2006.
3. R.Schmitt. FCC catalyst finds three safe reuse outlets in Europe. Oil & Gas Journal. 1991.
4. Hsiu Liang Chen, Yun Sheng Tseng, Kung Chung Hsu. Spent FCC catalyst as a pozzolanic material for high- performance mortars. Cement and Concrete Composites. 2004; 26(6): p. 657 - 664.
5. J.Monzó, J.Payá, M.V.Borrachero, E.Mora, S.Velázquez. Fluid catalytic cracking residue (FC3R) as a new pozzolanic material: Thermal analysis monitoring of FC3R/ Portland cement reactions. 7th CANMET/ACI International Conference on Fly Ash, Silica Fume, Slag and Natural Pozzolans in Concrete, India. 22 - 27 July, 2001.
6. B.Pacewska, I.Wilińska, J.Kubissa. Use of spent catalyst from catalytic cracking in fluidized bed as a new concrete additive. Thermochimica Acta. 1998; 322(2): p. 175 - 181.
7. B.Pacewska, M.Bukowsk, I.Wilińska, M.Swat. Modification of the properties of concrete by a new pozzolan - a waste catalyst from the catalytic process in a fluidized bed. Cement and Concrete Research. 2002; 32(1): p. 145 - 152.
8. L.Alonso, J.M.Palacios, E.García, R.Moliner. Characterization of Mn and Cu oxides as regenerable sorbents for hot coal gas desulfurization. Fuel Processing Technology. 2000; 62(1): p. 31 - 44.
9. Hans Zeiringer. Preparation of abrasive material from spent catalysts. US Patent 4142871 A. 1979.
10. Đỗ Quang Minh, Trần Bá Việt. Công nghệ sản xuất xi măng poóc lăng và các chất kết dính vô cơ. Nhà xuất bản Đại học Quốc gia Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh. 2007.
11. Brian McGrath. Reuse of spent oil catalyst in the manufacture of cement. IQA-CCAA Construction Material Industry Conference. 19 - 22 September, 2012.
12. J.Payá, J.Monzó, M.V.Borrachero, S.Velázquez. Evaluation of the pozzolanic activity of fluid catalytic cracking catalyst residue (FC3R). Thermogravimetric analysis studies on FC3R-Portland cement pastes. Cement and Concrete Research. 2003; 33(4): p. 603 - 609.
13. S.K.Antiohos, E.Chouliara, S.Tsimas. Re-use of spent catalyst from oil-cracking refineries as supplementary cementing material. China Particuology. 2006; 4(2): p. 73 - 76.
14. N.T.Castellanos, J.T.Agredo. Using spent fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) catalyst as pozzolanic addition - A review. 2010; 30(2): p. 35 - 42.
15. N.Su, Z.-H.Chen, H.-Y.Fang. Reuse of spent catalyst as fine aggregate in cement mortar. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2001; 23(1): p. 111 - 118.
16. J.Monzó, J.Payá, M.V.Borrachero, S.Velázquez, L.Soriano, J.Rigueira. Reusing of spent FCC catalyst as a very reactive pozzolanic material: Formulation of high performance concretes. International RILEM Conference on the Use of Recycled Materials in Buildings and Structures, Spain. 8 - 11 November, 2004.
17. Mei-in Melissa Chou, Luming Chen, Sheng Fu Joseph Chou. Spent equilibrium catalyst for manufacturing fired bricks: A commercial production demonstration. International Journal of Environmental Sustainability. 2013; 8(3): p. 19 - 35.
1. The Author assigns all copyright in and to the article (the Work) to the Petrovietnam Journal, including the right to publish, republish, transmit, sell and distribute the Work in whole or in part in electronic and print editions of the Journal, in all media of expression now known or later developed.
2. By this assignment of copyright to the Petrovietnam Journal, reproduction, posting, transmission, distribution or other use of the Work in whole or in part in any medium by the Author requires a full citation to the Journal, suitable in form and content as follows: title of article, authors’ names, journal title, volume, issue, year, copyright owner as specified in the Journal, DOI number. Links to the final article published on the website of the Journal are encouraged.




