Combining low frequency spectral decomposition and post-stack seismic inversion to identify Middle Miocene gas bearing sands at Hai Thach field
Abstract
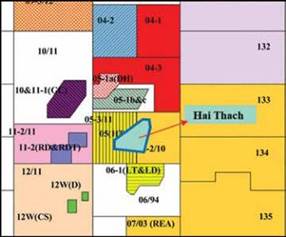
Located in the Nam Con Son basin, offshore Vietnam, Middle Miocene gas bearing turbidite sands at Hai Thach field are very difficult to identify on conventional seismic data due to their complex architectures and geometries [1]. The purpose of this study is mapping this reservoir in terms of its geometry and distribution by applying an integration of rock physics analysis, seismic attributes and post-stack seismic inversion. In the study areas, the P-impedance of sand is the same values with shale and the presence of gas in sand causes a decrease of acoustic impedance, which can be used to differentiate gas saturated sandstone from water saturated sandstone and shale. Seismic attributes applied based on the rock physics analysis result can also be used to define gas sand distributions. Low-frequency amplitude anomalies from 17 - 19Hz, obtained from spectral decomposition, have a high gas content where penetrated by wells, whereas low gas saturation zones in the wells do not correlate with the observed high amplitudes. Moreover, the gas sand distribution was successfully identified in the extracted P-impedance slice along horizon from an inverted P-impedance volume. Thus, the combination of low frequency spectral decomposition and seismic inversion may be used to successfully map gas distribution. Proposed workflow for mapping sand and gas sand can be used for future drilling programmes.
References
basin. Petrovietnam Journal. 2013; 10: p. 26 - 31.
2. CCOP. Vietnam petroleum geology and potential. 2002.
3. Naseer Ahmad, P. Rowell. Mapping of fluvial sand systems using rock physics analysis and simultaneous inversion for density: Case study from the Gulf of Thailand.
First Break. 1973; 31(5): p. 49 - 54.
4. Bagus Priyanto. Lithology prediction using rock physics analysis and seismic inversion within Miocene fluvial reservoir interval in the Songkhla basin, Gulf of Thailand.
Chulalongkorn University. 2012.
5. John P.Castagna, Shengjie Sun, Robert W.Siegfried. Instantaneous spectral analysis: Detection of low-frequency
shadows associated with hydrocarbons. The Leading Edge. 2003; 22(2): p. 120 - 127.
6. Abhinav Kumar Dubey. Reservoir characterization using AVO and seismic inversion techniques. The 9th Biennial International Conference & Exposition on Petroleum
Geophysics. 2012.
7. Jesus M.Rodriguez. Spectral decomposition and inversion: Case study of a production area in the Cook Inlet basin, Alaska, USA. University of Houston. 2009.
8. Mayura Dangprasitthiporn. Lithology prediction using rock physics and acoustic impedance for reservoir distribution in Northern Pattani basin, Gulf of Thailand.
Chulalongkorn University. 2015.
9. Patricia E.Gavotti, Don C.Lawton, Gary F.Margrave, J.Helen Isaac. Post-stack inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data. 2013.
1. The Author assigns all copyright in and to the article (the Work) to the Petrovietnam Journal, including the right to publish, republish, transmit, sell and distribute the Work in whole or in part in electronic and print editions of the Journal, in all media of expression now known or later developed.
2. By this assignment of copyright to the Petrovietnam Journal, reproduction, posting, transmission, distribution or other use of the Work in whole or in part in any medium by the Author requires a full citation to the Journal, suitable in form and content as follows: title of article, authors’ names, journal title, volume, issue, year, copyright owner as specified in the Journal, DOI number. Links to the final article published on the website of the Journal are encouraged.




