Evolution characteristics of shale diapir in the centre of Song Hong basin
Abstract
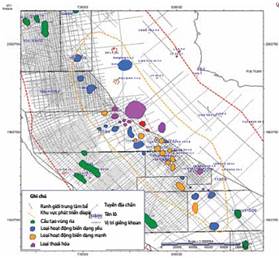
Cenozoic deposits in the centre of Song Hong basin (spreading from block 109 to block 115) have a great thickness, which can reach the depth of over 17km. The gas discoveries in this area (such as Bao Vang, Bao Trang, Bao Den, and Cua Lo) are all gas and condensate, and mainly related to the shale diapir formation. The diapirism has taken a very important role in the petroleum system of the centre of Song Hong basin. It is one of the factors to form traps and create migration pathway for gas to move upward to shallow sections along the development process of diapirs.
The cause of diapirism is the releasing of high pressure which existed in the deep area of the basin in late Miocene, early Pliocene and continues to recent time. The high pressure in Song Hong basin may be caused by some reasons including high geothermal gradient, high sedimentation rate in Miocene, Pliocene with mainly fine grain sediment and mudstone and the expulsion of hydrocarbon from Oligocene, Miocene source rocks.
References
2. Nguyễn Thị Dậu và nnk. Đánh giá tiềm năng dầu khí bể Sông Hồng. Viện Dầu khí Việt Nam. 2012.
3. Nguyễn Tiến Thịnh và nnk. Nghiên cứu sự hình thành tích tụ dầu khí trong trầm tích Miocen muộn - Pliocen khu vực trung tâm bể Sông Hồng. Viện Dầu khí Việt Nam.
2017: 152 trang.
4. B.J.Huang, X.M.Xiao, W.L.Dong. Multiphase natural gas migration and accumulation and its relationship to diapir structures in the DF1-1 gas field, South China Sea.
Marine and Petroleum Geology. 2002; 19(7): p. 861 - 872.
5. Chao Lei, Jianye Ren, Peter D.Clift, Zhenfeng Wang, Xusheng Li, Chuanxin Tong. The structure and formation of diapirs in the Yinggehai - Song Hong basin. Marine and
Petroleum Geology. 2011; 28 (5): p. 980 - 991.
6. Di Peng, Huang Hua, Huang Bao, He Jia, Chen Duo. Seabed pockmark formation associated with mud diapir development and fluid activities in the Yinggehai basin.
Journal of Tropical Oceanography. 2012; 31(5): p. 26 - 36.
7. R.E.Chapman. Chapter 15: Diapirs, diapirism and growth structures. Developments in Petroleum Science. 1983; 16: p. 325 - 348.
8. Christopher K.Morley, G.Guerin. Comparison of gravity-driven deformation styles and behavior associated with mobile shales and salt. Tectonics. 1996; 15(6): p.1154
- 1170.
9. B.C.Vendeville, M.P.A.Jackson. The rise of diapirs during thin-skinned extension. Marine and Petroleum Geology. 1992; 9(4): p. 331 - 354.
10. Lyobomir I.Dimitrov. Mud volcanoes-the most important pathway for degassing deeply buried sediments. Earth-Science Reviews. 2002; 59(1 - 4): p. 49 - 76.
11. A.Mazzini. Mud volcanism: Processes and implications. Marine and Petroleum Geology. 2009; 26(9): p.1677 - 1680.
12. A.Mazzini, A.Nermoen, M.Krotkiewski, Y.Podladchikov, S.Planke, H.Svensen. Strike-slip faulting as a trigger mechanism for overpressure release through piercement structures. Implications for the Lusi Mud Volcano, Indonesia. Marine and Petroleum Geology. 2009; 26(9): p. 1751 - 1765.
13. P.Van Rensbergen, C.K.Morley, D.W.Ang, T.Q.Hoan, N.T.Lam. Structural evolution of shale diapirs from reactive rise to mud volcanism: 3D seismic data from the baram delta, offshore Brunei Darussalam. Journal of the Geological Society. 1999; 156: p. 633 - 650. 14. Marco Bonini. Mud volcanoes: Indicators of stress orientation and tectonic controls. Earth-Science Reviews. 2012; 115(3): p. 121 - 152.
15. Siman A.Stewart, Richard J.Davies. Structure and emplacement of mud volcano systems in the South Caspian basin. AAPG Bulletin. 2006; 90(5): p. 771 - 786.
16. Xinong, Xie, Li Sitian, Dong Weiliang, Zhang Qiming. Overpressure development and hydrofracturing in the Yinggehai basin. Journal of Petroleum Geology. 1999;
22(4): p. 437 - 454.
17. Lijuan He, Liangping Xiong, Jiyang Wang. Heat flow and thermal modeling of the Yinggehai basin. Tectonophysics. 2002; 351(3): p. 245 - 253.
18. Yusong Yuan, Weilin Zhu, Lijun Mi, Gongcheng Zhang, Shengbiao Hu, Lijuan He. Uniform geothermal gradient” and heat flow in the Qiongdongnan and Pearl river
Mouth basins. Marine and Petroleum Geology. 2009; 26(7): p. 1152 - 1162.
19. Xuan-Ce Wang, Zheng-Xiang Li, Xian-Hu Li, Jie Li, Yung Liu, Wen-Guo Long, JIn-Bo Zhou, Fei Wang. Temperature, pressure, and composition of the mantlesource region of late Cenozoic basalts in Hainan island, SE
Asia: A consequence of a young thermal mantle plume close to subduction zones? Journal of Petrology. 2012; 53(1): p. 177 - 233.
20. Xinong Xie, Li Sitian, Dong Weiliang, Zhang Qiming. Overpressure development and hydrofracturing in the Yinggehai basin. Journal of Petroleum Geology. 1999; 22(4): p. 437 - 454.
1. The Author assigns all copyright in and to the article (the Work) to the Petrovietnam Journal, including the right to publish, republish, transmit, sell and distribute the Work in whole or in part in electronic and print editions of the Journal, in all media of expression now known or later developed.
2. By this assignment of copyright to the Petrovietnam Journal, reproduction, posting, transmission, distribution or other use of the Work in whole or in part in any medium by the Author requires a full citation to the Journal, suitable in form and content as follows: title of article, authors’ names, journal title, volume, issue, year, copyright owner as specified in the Journal, DOI number. Links to the final article published on the website of the Journal are encouraged.




