Conversion of sustainable agricultural residues into MCC for PLA-based biodegradable plastic applications
Abstract
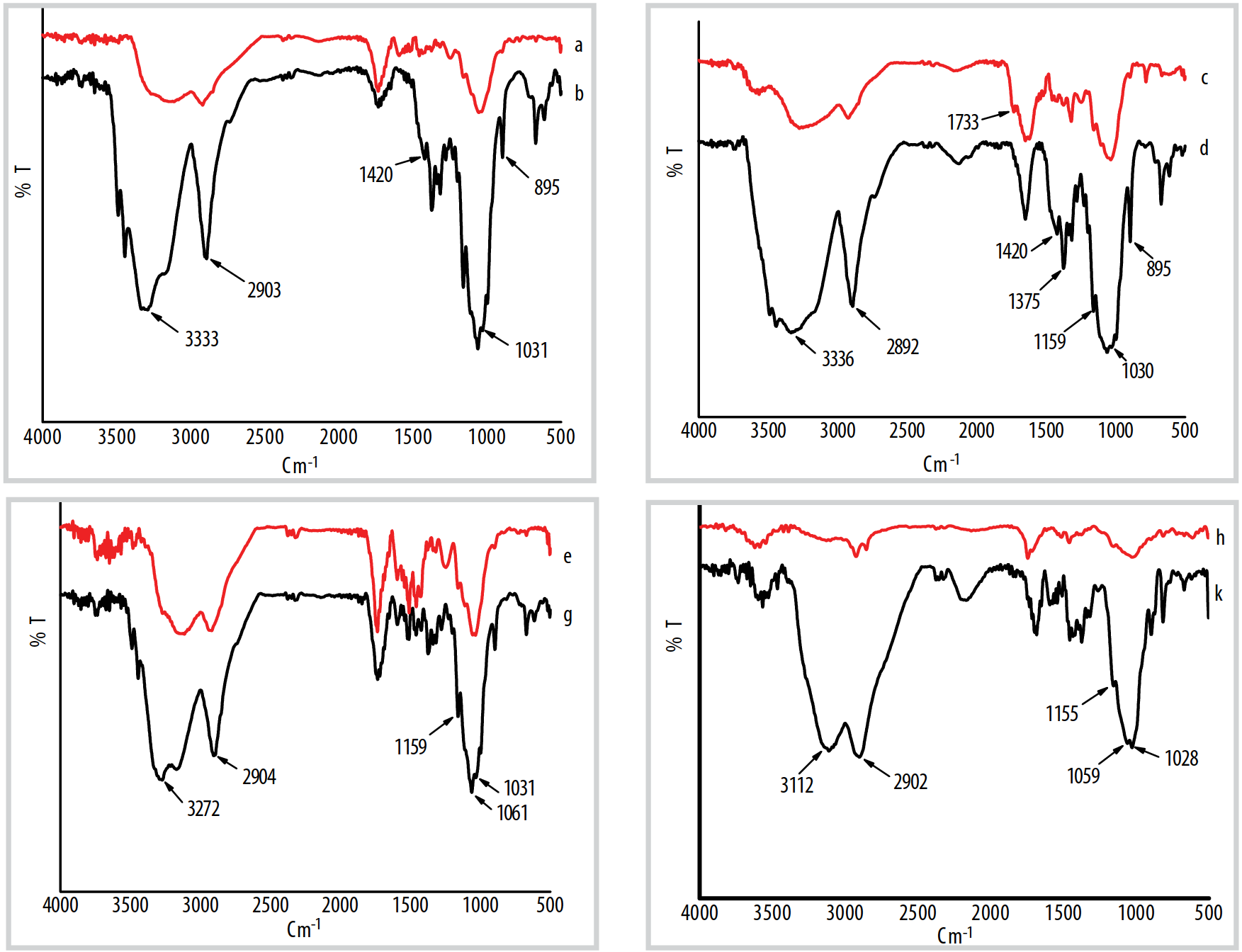
Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) was extracted from cassava stems, banana pseudostems, pineapple leaves, and spent coffee grounds through an optimized acid hydrolysis process. Comprehensive structural, morphological, and thermal characterization revealed distinct differences among sources, with cassava stem-derived MCC identified as the most feasible and sustainable option due to its high crystallinity, uniform particle size, processing stability, ready availability, and large-scale supplypotential. This MCC was incorporated into thermoplastic starch (TPS) and polylactic acid (PLA) matrices to fabricate fully biodegradable composites. X-ray diffraction (XRD) confirmed the preservation of MCC crystalline structure, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) revealed homogeneous dispersion within the TPS phase, and thermogravimetric/differential thermal analyses (TGA/DTA) demonstrated improved thermal stability. Mechanical testing showed that the optimized PLA:MCC:TPS ratio of 70:4.5:25.5 (with 15% MCC relative to (MCC/TPS)) provided the best balance between tensile strength, modulus, and biodegradability.These composites exhibited mechanical strength for sustainable packaging and food service applications while maintaining full compostability. Overall, the results highlight cassava stems as a sustainable, locally available MCC source and confirm that PLA/(MCC/TPS) composites can replace petrochemical-based plastics in targeted sectors, contributing to global energy transition strategies and CO2 emission reduction targets.
References
Naved Azum, Mohammad Jawaid, Lau, Kia Kian, Anish Khan, and Maha Moteb Alotaibi, “Extraction of microcrystalline cellulose from Washingtonia fibre and its characterization”, Polymers, Volume 13, Issue 18, 2021. DOI: 10.3390/polym13183030.
C. Uma Maheswari, K. Obi Reddy, E. Muzenda, B. Guduri, and A. Varada Rajulu, “Extraction and characterization of cellulose microfibrils from agricultural residue - Cocos nucifera L”, Biomass and Bioenergy, Volume 46, pp. 555 - 563, 2012. DOI: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.06.039.
P. Nehra and R.P. Chauhan, “Facile synthesis of nanocellulose from wheat straw as an agricultural waste”, Iranian Polymer Journal, Volume 31, Issue 6, pp. 771 - 778, 2022. DOI:10.1007/s13726-022-01040-0.
Mohd Yussni Hashim, Azriszul Mohd Amin, Omar Mohd Faizan Marwah, Mohd Hilmi Othman, Mohd Radzi Mohamed Yunus, and Ng Chuan Huat, “The effect of alkali treatment under various conditions on physical properties of kenaf fiber”, Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Volume 914, 2017. DOI: 10.1088/1742-6596/914/1/012030.
Selwin Maria Sekar, Rajini Nagarajan, Ponsuriyaprakash Selvakumar, Nadir Ayrilmis, Kumar Krishnan, Faruq Mohammad, Hamad A. Al-Lohedan, and Sikiru O. Ismail, "3D-printed green biocomposites from poly(lactic acid) and pine wood-derived microcrystalline cellulose: Characterization and properties", BioResources, Volume 20, Issue 4, pp. 8473 - 8492, 2025. DOI: 10.15376/biores.20.4.8473-8492.
M.K. Mohamad Haafiz, Azman Hassan, Zainoha Zakaria, I.M. Inuwa, M.S. Islam, M. Jawaid, “Properties of polylactic acid composites reinforced with oil palm biomass microcrystalline cellulose”, Carbohydrate Polymers, Volume 98, Issue 1, 15, pp. 139 - 145, 2013.
Nanang Triyono, Fatma Sari, Ika Kurniaty, Ratri Ariatmi Nugrahani, Tri Yuni Hendrawati, and Susanty, “Characterization of microcrystalline cellulose from cassava stems through acid hydrolysis process using H2SO4 with variation concentration”, International Conference on Engineering, Construction, Renewable Energy, and Advanced Materials, Fakultas Teknik Universitas Muhammadiyah Jakarta, 30 April 2024.
Jie Chen, Xia Wang, Zhu Long, Shuangfei Wang, Jingxian Zhang, and Lei Wang, “Preparation and performance of thermoplastic starch and microcrystalline cellulose for packaging composites: Extrusion and hot pressing”, International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, Volume 165, pp. 2295 - 2302, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.117.
Daniele Rigotti, Luca Fambri, Alessandro Pegoretti, “Bio composites for fused filament fabrication: effects of maleic anhydride grafting on poly(lactic acid) and microcellulose”, Progress in Additive Manufacturing, Volume 7, pp. 765 - 783, 2022. DOI: 10.1007/s40964-022-00264-z.
Nehemiah Mengistu Zeleke, Devendra Kumar Sinha, and Getinet Asrat Mengesha, “Chemical composition and extraction of micro crystalline cellulose from outer skin isolated coffee husk”, Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2022. DOI: 10.1155/2022/7163359.
Wei Sing Yong, Yee Lee Yeu, Ping Ping Chung, and Kok Heng Soon, “Extraction and characterization of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) from durian rind for biocomposite application”, Journal of Polymers and the Environment, Volume 32, pp. 6544 - 6575, 2024. DOI: 10.1007/s10924-024-03401-7.
Yanlan Liu, Jingfeng Ran, Ziyang Xu, Hao Cheng, Benping Lin, Tianran Deng, and Cuiping Yi, “Preparation and characterization of microcrystalline cellulose from rice bran”, Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, Volume 105, Issue1, pp. 218 - 226, 2025. DOI: 10.1002/jsfa.13820.
Xutong Wang, Xiaoqiang Cui, Yuechi Che, Shengquan Zhou, Zeng Dan, Beibei Yan, Guanyi Chen, and Ting Wang, “Gasification of Tibetan herb residue: Thermogravimetric analysis and experimental study”, Biomass and Bioenergy, Volume 146, 2021. DOI: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2020.105952.
Raquel S. Reis, Lucas G.P. Tienne, Diego de H.S. Souza, Maria de Fátima V. Marques, and Sergio N. Monteiro, “Characterization of coffee parchment and innovative steam explosion treatment to obtain micro - brillated cellulose as potential composite reinforcement”, Journal of Materials Research and Technology, Volume 9, Issue 4, pp. 9412 - 9421, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.05.099.
Putri Nawangsari, Warman Fatra, Aryandi Kusuma, Muftil Badri, Dedi Rosa P.C, and Dedy Masnur, “Microcellulose from pineapple leaf Fiber as a potential sustainable material: Extraction and characterization”, Journal Polimesin, Volume 22, Issue 1, 2024.
Sataporn Malarat, Dilawin Khongpun, Kanokkorn Limtong, Napasin Sinthuwong, Pornpinun Soontornapaluk, Chularat Sakdaronnarong, and Pattaraporn Posoknistakul, “Preparation of nanocellulose from coffee pulp and its potential as a polymer reinforcement”, ACS Omega, Volume 8, Issue 28, pp. 25122 - 25133, 2023. DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c02016.
Djalal Trache, André Donnot, Kamel Khimeche, Riad Benelmir, and Nicolas Brosse, “Physico-chemical properties and thermal stability of microcrystalline cellulose isolated from alfa fibres”, Carbohydrate Polymers, Volume 104, pp. 223 - 230. 2014. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.01.058.
1. The Author assigns all copyright in and to the article (the Work) to the Petrovietnam Journal, including the right to publish, republish, transmit, sell and distribute the Work in whole or in part in electronic and print editions of the Journal, in all media of expression now known or later developed.
2. By this assignment of copyright to the Petrovietnam Journal, reproduction, posting, transmission, distribution or other use of the Work in whole or in part in any medium by the Author requires a full citation to the Journal, suitable in form and content as follows: title of article, authors’ names, journal title, volume, issue, year, copyright owner as specified in the Journal, DOI number. Links to the final article published on the website of the Journal are encouraged.




